Bariatric surgery in Malaysia provides evidence-based, MOH-regulated treatment for severe obesity and metabolic disease. Using Asian-specific BMI criteria, fellowship-trained surgeons perform procedures such as sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass with expected 60–70% excess weight loss. Costs typically range from RM25,000–RM45,000 with structured long-term follow-up.
Bariatric surgery in Malaysia is a medically approved treatment for severe obesity using procedures such as sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass. Eligible patients (BMI ≥32.5 Asian criteria) typically lose 60–70% of excess weight within 18–24 months. Surgery costs range from RM25,000 to RM45,000 depending on procedure and hospital.
Key Takeaways
Eligibility: BMI ≥32.5 kg/m² with obesity-related disease or BMI ≥37.5 kg/m² regardless of comorbidities
Main Procedures: Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
Weight Loss: 60–70% excess weight loss within 12–24 months
Metabolic Benefits: Significant improvement or remission of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea
Cost: RM25,000–RM45,000 depending on complexity and facility
Recovery: 2–3 days hospital stay, return to work in 2–3 weeks
Long-Term Success: >90% achieve ≥50% excess weight loss with structured follow-up
Understanding Bariatric Surgery: Medical and Metabolic Foundation
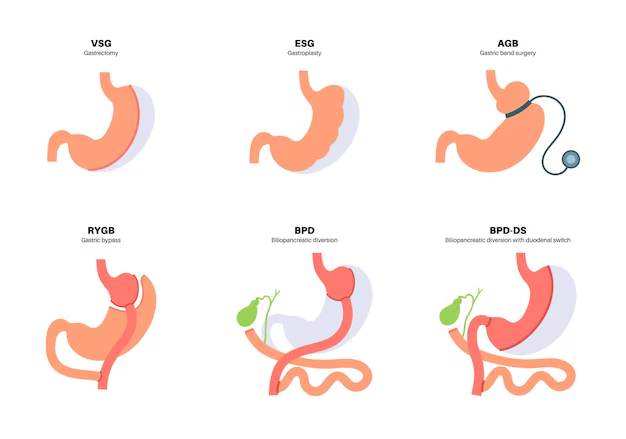
Bariatric surgery, also referred to as metabolic surgery, consists of surgical procedures designed to treat severe obesity and its associated metabolic diseases. These procedures alter gastrointestinal anatomy to achieve sustained weight loss and hormonal regulation.
Unlike cosmetic weight-loss methods, bariatric surgery is a medically indicated treatment recognised by international bodies including IFSO, ASMBS, and the Asia-Pacific Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery Society.
Mechanisms of Action
Bariatric surgery works through three primary mechanisms:
Restriction – reduces stomach capacity, limiting food intake
Hormonal Modulation – decreases hunger hormones (especially ghrelin) and improves insulin sensitivity
Malabsorption (select procedures) – limits calorie and nutrient absorption
These changes explain why surgery consistently outperforms diet and medication alone for long-term obesity management.
Asian-Specific Obesity Classification
Asian populations develop metabolic diseases at lower BMI levels due to higher visceral fat and insulin resistance. Malaysia follows adjusted thresholds:
BMI ≥32.5 kg/m² with obesity-related disease
BMI ≥37.5 kg/m² regardless of comorbidities
This approach aligns with regional consensus guidelines and improves early intervention outcomes.
Who Qualifies for Bariatric Surgery in Malaysia?
Eligibility is determined through a multidisciplinary assessment involving surgeons, physicians, dietitians, and psychologists.
Primary Eligibility Criteria
You may qualify if you have:
Type 2 diabetes
Hypertension
Dyslipidemia
Obstructive sleep apnea
MASLD (fatty liver disease)
Heart or kidney disease
Severe joint disease affecting mobility
Patients must also demonstrate failed supervised weight-loss attempts for at least 6 months.
Additional Medical Requirements
Psychological evaluation to confirm readiness for lifestyle change
Nutritional assessment and correction of deficiencies
Smoking, alcohol, and substance cessation prior to surgery
Age typically between 18–65 years (case-by-case exceptions apply)
Pre-Surgical Medical Screening
Before surgery, patients undergo comprehensive testing:
Full blood count and metabolic panel
Liver and kidney function tests
ECG and cardiac evaluation
Sleep study (if apnea suspected)
Upper endoscopy
Nutritional deficiency screening
These tests establish safety, optimise outcomes, and reduce peri-operative risks.
Types of Bariatric Surgery Available in Malaysia
Most bariatric procedures in Malaysia are performed laparoscopically, offering faster recovery, smaller incisions, and reduced complication rates.
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG)
Sleeve gastrectomy removes approximately 75–80% of the stomach, forming a narrow gastric tube.
Benefits:
Significant appetite reduction
Lower ghrelin hormone production
No intestinal bypass
Lower long-term vitamin deficiency risk
Expected Outcomes:
60–70% excess weight loss
Strong improvement in insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome
This is the most commonly performed bariatric procedure in Malaysia in 2026.
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)
Gastric bypass creates a small gastric pouch and reroutes food to the lower small intestine.
Advantages:
Strong appetite suppression
Highest diabetes remission rates
Effective for severe reflux disease
Considerations:
Lifelong vitamin supplementation required
Higher nutritional monitoring needs
Studies published in JAMA Surgery show diabetes remission in over 60% of patients at 5 years.
Advanced Procedures: BPD/DS and SADI-S
Reserved for patients with very high BMI (>50) or complex metabolic disease.
| Procedure | Excess Weight Loss | Diabetes Remission | Vitamin Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sleeve Gastrectomy | 60–70% | Moderate–High | Low–Moderate |
| Gastric Bypass | 65–75% | High | Moderate–High |
| BPD/DS / SADI-S | 70–80% | Very High | High |
Revision Bariatric Surgery
Revision surgery addresses inadequate weight loss, weight regain, reflux, or complications from prior procedures.
Common revisions include:
Band to sleeve or bypass
Sleeve to gastric bypass
Correction of pouch dilation
These procedures require high surgical expertise and careful patient selection.
Is Bariatric Surgery Safe?
Modern bariatric surgery has safety profiles comparable to gallbladder surgery or joint replacement.
Short-Term Risks (Overall <5%)
Bleeding
Infection
Blood clots
Anastomotic leaks
Hernias
Risk is significantly lower in high-volume centers with experienced teams.
Long-Term Considerations
Nutritional deficiencies
Dumping syndrome (mainly bypass)
Gallstones due to rapid weight loss
Excess skin
Lifelong monitoring mitigates nearly all long-term risks.
Cost of Bariatric Surgery in Malaysia (2026)
Average Price Ranges
Sleeve Gastrectomy: RM28,000–RM38,000
Gastric Bypass: RM32,000–RM45,000
BPD/DS or SADI-S: RM40,000–RM55,000
Revision Surgery: RM35,000–RM50,000
Additional Costs
Pre-operative tests: RM2,000–RM5,000
Vitamins and supplements: RM100–RM200/month
Follow-up blood tests
Optional body contouring surgery
Insurance Coverage in Malaysia
Most local policies exclude bariatric surgery unless strict medical necessity is proven. Some corporate or international plans offer partial coverage.
Approval improves with:
Documented obesity-related disease
Long-term failed medical therapy
Specialist letters
Pre-authorization requests
Recovery and Weight Loss Timeline
Hospital Stay
2–3 days (sometimes 1 day)
Return to Work
Desk work: 2 weeks
Physical jobs: 4–6 weeks
Weight Loss Phases
0–3 months: Rapid loss (15–25 kg common)
3–12 months: Steady metabolic loss
12–24 months: Plateau and stabilization
Most patients reach lowest weight by 18–24 months.
Long-Term Success and Maintenance
Success is defined as:
≥50% excess weight loss
Sustained metabolic improvement
Normal regain:
5–10% of lost weight
Prevention strategies:
Protein-first nutrition
Regular exercise (150 min/week)
Lifelong vitamin compliance
Scheduled follow-ups
Health Benefits Beyond Weight Loss
Type 2 Diabetes: 60–80% remission or improvement
Hypertension & Cholesterol: Reduced medication needs
Sleep Apnea: CPAP often discontinued
Joint Pain: Improved mobility
Fatty Liver Disease: Reversal common
Special Considerations for Malaysian Patients
Asian-specific BMI thresholds
Cultural dietary adaptation
Ramadan fasting guidance post-recovery
Halal-certified supplements
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How much weight can I lose with bariatric surgery in Malaysia?
Most patients lose 60–70% of excess body weight within 18–24 months after sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass. For someone 50 kg above ideal weight, this equals about 30–35 kg loss. Results vary by procedure, lifestyle adherence, and metabolic health, but long-term success exceeds 90% with follow-up care.
2. Will insurance cover bariatric surgery in Malaysia?
Most Malaysian insurance plans do not cover bariatric surgery, classifying it as elective. Some corporate or international policies may approve coverage if surgery is medically necessary. Approval requires BMI records, failed weight-loss history, comorbidities, specialist letters, and pre-authorization. Coverage is not guaranteed.
3. Can bariatric surgery cure type 2 diabetes?
Bariatric surgery can induce diabetes remission in 60–80% of patients, especially after gastric bypass. However, it is considered remission, not a cure, as diabetes may return with weight regain or disease progression. Best results occur in patients with diabetes under 10 years duration.
4. How do I choose between sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass?
Sleeve gastrectomy suits patients seeking effective weight loss with simpler follow-up and lower vitamin risk. Gastric bypass is preferred for severe diabetes, reflux disease, or higher BMI, offering stronger metabolic effects. Both procedures achieve over 90% success for excess weight loss when properly selected.
5. What if I don’t lose enough weight or regain weight after surgery?
About 15–20% of patients experience inadequate loss or weight regain. First-line treatment includes dietary counseling, behavioral therapy, exercise support, and medication if needed. Revision surgery is considered only when anatomical issues exist. Regain of 5–10% is normal and acceptable long-term.
Final Thoughts
Bariatric surgery is not a shortcut. It is a scientifically proven medical intervention for patients whose biology resists conventional weight loss.
For patients with severe obesity, surgery offers something diets cannot: metabolic reset, hormonal balance, and long-term disease control.
When combined with structured follow-up, bariatric surgery in Malaysia delivers durable weight loss, improved longevity, and restored quality of life.


