Is Bariatric Surgery Right for You? Best Weight Loss Surgery in Malaysia
Bariatric Surgery & Weight Loss Surgery Malaysia What Is Bariatric Surgery? Bariatric surgery encompasses a group of procedures designed to aid weight loss by altering the digestive system. These surgeries limit food intake, reduce nutrient absorption, or both. Popular types of bariatric surgery include: Gastric Sleeve Surgery: Removes a large portion of the stomach, reducing its size and limiting food intake. Gastric Bypass Surgery: Creates a small stomach pouch and reroutes the intestines to decrease calorie and nutrient absorption. Adjustable Gastric Banding: Places a band around the upper stomach to create a smaller stomach pouch. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS): A less common but highly effective surgery combining gastric sleeve and intestinal bypass. Is Bariatric Surgery Right for You? Bariatric surgery is not a quick fix but a powerful tool for those who meet specific criteria. Consider the following factors: 1. Body Mass Index (BMI) A BMI of 40 or higher typically qualifies an individual for surgery. A BMI of 35-39.9 with obesity-related conditions like diabetes or hypertension may also qualify. 2. Failed Weight Loss Attempts Surgery is usually recommended for individuals who have tried and failed to achieve lasting weight loss through diet, exercise, and medical treatments. 3. Health Conditions Bariatric surgery can improve or resolve conditions such as type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and joint pain. 4. Commitment to Lifestyle Changes Success requires long-term dietary changes, regular exercise, and routine medical follow-ups. 5. Mental Health Evaluation Candidates must be prepared for the psychological and emotional aspects of surgery. A mental health evaluation is often part of the pre-surgery process. Benefits of Bariatric Surgery Bariatric surgery offers life-changing benefits beyond weight loss: Improved Health: Resolves or reduces the severity of many obesity-related diseases. Enhanced Quality of Life: Increases mobility, energy levels, and self-confidence. Longevity: Reduces the risk of premature death associated with obesity. Risks and Considerations Like any surgical procedure, bariatric surgery carries risks. These may include: Infection or bleeding Nutritional deficiencies Dumping syndrome (common in gastric bypass patients) Emotional and psychological adjustments Choosing a qualified surgeon and adhering to post-surgery guidelines significantly minimizes these risks. Best Weight Loss Surgery Options in Malaysia Malaysia is emerging as a hub for high-quality, affordable bariatric surgery. With advanced medical facilities, skilled surgeons, and competitive pricing, it’s an excellent destination for both local and international patients. Here are some popular weight loss surgery options available in Malaysia: 1. Gastric Sleeve Surgery Overview: Reduces stomach size by removing up to 80% of the stomach. Benefits: Simpler procedure with fewer risks compared to gastric bypass. Hospitals Offering This Surgery: Many private hospitals in Kuala Lumpur, such as Prince Court Medical Centre and Gleneagles Hospital. 2. Gastric Bypass Surgery Overview: Involves creating a small pouch and rerouting the intestines. Benefits: Offers rapid and significant weight loss. Availability: Available at leading bariatric centers in Malaysia. 3. Adjustable Gastric Banding Overview: Involves placing an adjustable band around the stomach. Benefits: Less invasive and reversible. Drawbacks: May result in slower weight loss compared to other surgeries. 4. Mini Gastric Bypass (MGB) Overview: A simpler and shorter version of traditional gastric bypass. Benefits: Faster recovery with effective weight loss. Ideal Candidates: Patients seeking a middle ground between gastric sleeve and bypass. Choosing the Right Bariatric Surgeon in Malaysia To ensure a safe and successful experience, it’s crucial to choose a qualified and experienced surgeon. Look for: Accreditation: Ensure the hospital and surgeon are accredited by relevant medical boards. Experience: Opt for surgeons specializing in bariatric procedures with a proven track record. Patient Reviews: Read testimonials from previous patients to gauge satisfaction levels. Pre- and Post-Operative Support: Check for comprehensive care, including dietary counseling and psychological support. FAQs About Bariatric Surgery in Malaysia 1. How much does bariatric surgery cost in Malaysia? The cost varies based on the procedure and hospital but typically ranges from RM 30,000 to RM 60,000. This is significantly lower compared to many Western countries. 2. Is bariatric surgery covered by insurance in Malaysia? Coverage depends on your insurance policy. Some providers cover bariatric surgery if it’s deemed medically necessary. 3. How long is the recovery period? Recovery times vary. Most patients resume normal activities within 2-4 weeks, but full recovery can take up to 6 weeks. 4. Are there dietary restrictions after surgery? Yes. Patients must follow a strict diet, starting with liquids and gradually progressing to solid foods. Lifelong dietary adjustments are necessary to maintain results. 5. Can international patients undergo bariatric surgery in Malaysia? Absolutely. Malaysia’s medical tourism industry caters to international patients, offering personalized care and affordable packages. Conclusion Bariatric surgery is a life-changing decision that requires careful consideration and commitment. If you’re struggling with severe obesity and associated health issues, this surgery could be the key to a healthier and more fulfilling life. Malaysia stands out as a top destination for bariatric surgery, offering world-class care at an affordable cost. Consult with a qualified bariatric surgeon to explore your options and embark on a journey toward better health and wellness. With the right support and determination, bariatric surgery can be a powerful tool for transforming your life. View this post on Instagram A post shared by Bariatric Surgery Malaysia (@bariatricsurgerymalaysia)
Gastric Sleeve vs Gastric Bypass: What’s The Differences? Let’s Explore!
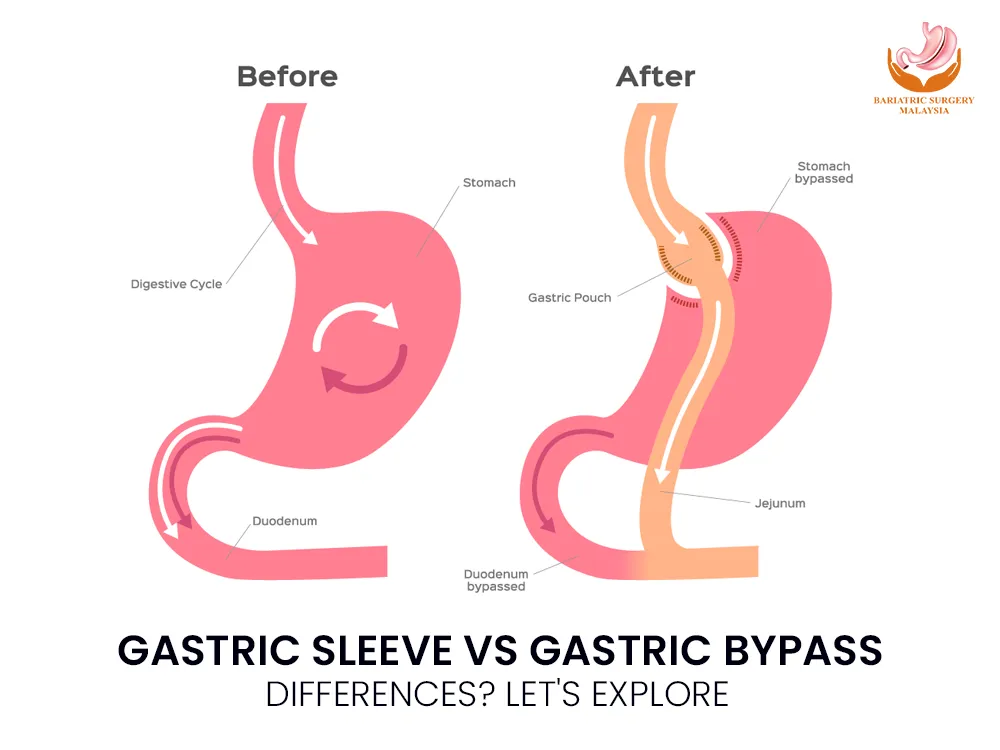
Gastric Sleeve vs Gastric Bypass Gastric Sleeve Vs Gastric Bypass – Obesity is a growing health challenge worldwide, leading many individuals to seek bariatric surgery as a sustainable solution for weight loss and improved health. Two of the most common procedures are gastric sleeve and gastric bypass. While both surgeries aim to help patients lose weight by altering the digestive system, they differ significantly in approach, benefits, and risks. What Is Gastric Sleeve Surgery? Also known as sleeve gastrectomy, gastric sleeve surgery involves the removal of approximately 75-80% of the stomach. The remaining portion is reshaped into a tube-like structure, resembling a banana. This significantly reduces the stomach’s capacity, limiting food intake and promoting early satiety. Moreover, the surgery lowers the production of ghrelin, the hunger hormone, aiding in appetite control. Benefits of Gastric Sleeve: Simpler procedure compared to gastric bypass. No rerouting of the intestines, reducing complication risks. Effective weight loss: Patients typically lose 50-60% of their excess weight within 18-24 months. Shorter surgery and recovery time. Drawbacks: Irreversible procedure. Limited effect on nutrient absorption, which may lead to slower weight loss compared to bypass. Risk of acid reflux or heartburn. What Is Gastric Bypass Surgery? Gastric bypass, formally known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is a more complex procedure. It involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach and directly connecting it to the small intestine, bypassing a significant portion of the stomach and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). This not only reduces the stomach’s capacity but also limits calorie and nutrient absorption. Benefits of Gastric Bypass: Significant and rapid weight loss: Patients can lose 60-80% of their excess weight within the first year. Effective in managing obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea. Long-lasting results for sustained weight loss. Drawbacks: Complex procedure with higher surgical risks. Requires lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation to prevent deficiencies. Potential for dumping syndrome (nausea, diarrhea, and fatigue after eating high-sugar foods). Differences Between Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass Aspect Gastric Sleeve Gastric Bypass Procedure Complexity Simpler, no rerouting of intestines More complex, involves intestine rerouting Weight Loss 50-60% of excess weight in 18-24 months 60-80% of excess weight within a year Reversibility Irreversible Partially reversible Nutrient Absorption Minimal impact Reduced nutrient absorption Risks Acid reflux, less dramatic weight loss Dumping syndrome, nutritional deficiencies Ideal Candidates Patients preferring a simpler procedure Patients with severe obesity or comorbidities Which Procedure Is Right for You? The choice between gastric sleeve and gastric bypass depends on several factors, including: Health Conditions: Gastric bypass is often recommended for patients with severe obesity-related conditions, as it is more effective in resolving these issues. Weight Loss Goals: Those seeking more dramatic weight loss may benefit from gastric bypass. Surgical Risk Tolerance: Gastric sleeve is a less invasive procedure with fewer surgical risks, making it suitable for patients wary of complications. Lifestyle and Commitment: Both surgeries require lifelong dietary changes, but gastric bypass demands stricter adherence to supplementation. Consulting with a bariatric surgeon and undergoing a thorough medical evaluation is essential to determine the best option for your individual needs. FAQs About Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass 1. How much weight can I expect to lose with each procedure? Gastric sleeve patients typically lose 50-60% of their excess weight within 18-24 months. Gastric bypass patients may lose 60-80% of their excess weight within the first year. 2. Are these surgeries safe? Both procedures are considered safe when performed by experienced surgeons. However, like any surgery, they carry risks such as infection, blood clots, or complications from anesthesia. 3. Will I need to take vitamins and supplements? Yes. Gastric bypass patients require lifelong supplementation due to reduced nutrient absorption. Gastric sleeve patients may also need supplements, but to a lesser extent. 4. Can either procedure be reversed? Gastric sleeve is irreversible because a large portion of the stomach is permanently removed. Gastric bypass can be reversed in rare cases, but the process is complex. 5. How long is the recovery period? Recovery time varies. Gastric sleeve patients often return to normal activities within 2-4 weeks, while gastric bypass patients may need 4-6 weeks to recover fully. Conclusion Choosing between gastric sleeve and gastric bypass is a significant decision that requires careful consideration of your health, weight loss goals, and lifestyle. Both procedures offer life-changing benefits, but they come with unique challenges. Consulting with a qualified bariatric surgeon can help you weigh the pros and cons to make the best choice for your journey toward a healthier life. Whether you opt for the simplicity of gastric sleeve or the transformative power of gastric bypass, committing to a healthier lifestyle is key to long-term success. View this post on Instagram A post shared by Bariatric Surgery Malaysia (@bariatricsurgerymalaysia)
Endoscopy Malaysia: Procedure, Types, What To Expect
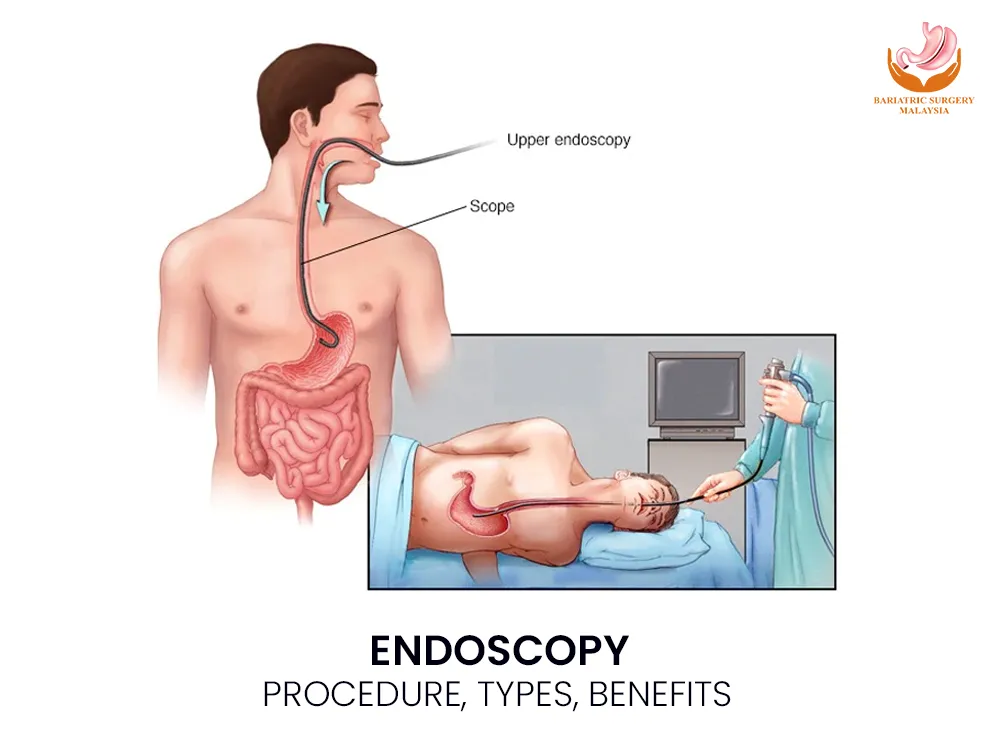
Endoscopy: Procedure, Types, What To Expect In Malaysia, over 30,000 endoscopy procedures are performed annually in both public and private hospitals, reflecting the growing demand for early detection of gastrointestinal diseases such as ulcers, polyps, and cancer. What Is Endoscopy? Endoscopy is a minimally invasive medical procedure that enables doctors to see inside the body without making large incisions. Using a flexible tube called an endoscope, equipped with a light and camera, doctors can examine internal organs in real time. It is used for both diagnostic purposes (to identify the cause of symptoms) and therapeutic purposes (to remove polyps, stop bleeding, or collect tissue samples for biopsy). Types of Endoscopy by Area Examined 1. Gastroscopy (Upper Endoscopy) Examines the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. Commonly used to detect acid reflux, ulcers, and stomach pain. 2. Colonoscopy Examines the colon and rectum. It is the gold standard for detecting polyps, colorectal cancer, and chronic bowel issues. 3. Sigmoidoscopy A shorter version of colonoscopy that focuses on the rectum and sigmoid colon. 4. Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Combines endoscopy with ultrasound imaging to assess nearby organs such as the pancreas and lymph nodes. 5. Capsule Endoscopy Involves swallowing a tiny capsule camera that takes thousands of images of the small intestine. 6. Bronchoscopy Used to examine the lungs and airways, especially in cases of persistent cough or lung disease. 7. ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) Evaluates the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, often used to treat gallstones or blockages. In Malaysia, the most common endoscopies are gastroscopy and colonoscopy due to the high prevalence of digestive issues and colorectal cancer. Endoscopy Procedure: Step by Step Step 1: Preparation Patients fast for 6–12 hours before the procedure. For colonoscopy, a bowel-cleansing solution is prescribed. Step 2: Sedation & Monitoring Mild sedation or anesthesia is administered through an IV line. Vital signs (heart rate, oxygen levels) are continuously monitored. Step 3: Insertion of Endoscope For gastroscopy, the tube is passed through the mouth into the stomach. For colonoscopy, it is inserted through the rectum into the colon. Step 4: Examination & Biopsy The doctor visually inspects the digestive tract. Tissue samples (biopsy) may be taken for analysis. Polyps or small growths can be removed immediately. Step 5: Recovery Patients rest for 30–60 minutes post-procedure. Temporary side effects may include mild bloating or sore throat. Most individuals resume normal activities within 24 hours. Types of Endoscopy in Malaysia & Their Uses Gastroscopy (Upper Endoscopy) Used to diagnose acid reflux (GERD), gastritis, peptic ulcers, stomach bleeding, and H. pylori infection. Can also detect early stomach cancer, which is more common in Asia. Colonoscopy The gold standard for colorectal cancer screening. Detects and removes polyps before they turn cancerous. Recommended for individuals aged 50 and above, or earlier if there is a family history. Sigmoidoscopy A shorter, quicker test than colonoscopy. Often used for patients with rectal bleeding or chronic constipation. Other Specialized Endoscopies EUS (Endoscopic Ultrasound): Helps stage cancer and assess pancreas or bile duct conditions. ERCP: Removes gallstones or places stents in bile ducts. Capsule Endoscopy: Ideal for investigating unexplained bleeding in the small intestine. Applications of Endoscopy Diagnostic Applications Detecting ulcers, gastritis, celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Identifying polyps, tumors, or early-stage cancer. Investigating chronic abdominal pain, anemia, or GI bleeding. Therapeutic Applications Removing polyps or small tumors. Stopping gastrointestinal bleeding using clips or cauterization. Dilating narrowed esophageal passages (strictures). Collecting biopsies for further diagnosis. Benefits of Endoscopy Minimally invasive: Avoids large surgical incisions. Highly accurate: Allows real-time visualization of the digestive tract. Quick recovery: Patients can usually go home the same day. Dual-purpose: Diagnoses and treats in a single session. Cancer prevention: Regular colonoscopy reduces colorectal cancer risk by up to 70% by detecting and removing polyps early. Risks & Safety Endoscopy is considered very safe, especially in MOH-certified hospitals and private clinics. Risks are rare but may include: Mild bloating, cramps, or sore throat (common but temporary). Bleeding (less than 1%). Perforation of the intestine or stomach (<0.1%). With proper preparation and experienced doctors, the benefits far outweigh the risks. Cost of Endoscopy in Malaysia The cost of endoscopy varies depending on the type, hospital, and whether it is done in a government or private facility. Gastroscopy: RM 800 – RM 2,000 Colonoscopy: RM 1,500 – RM 3,000 Sigmoidoscopy: RM 600 – RM 1,200 Capsule Endoscopy: RM 3,000 – RM 5,000 Government hospitals may be more affordable, but waiting times are longer. Private hospitals in Kuala Lumpur, Penang, and Johor Bahru provide faster access, often with advanced equipment. Preparation To ensure accurate results, patients should: Fast for 6–12 hours before the procedure. Follow bowel cleansing instructions for colonoscopy. Inform the doctor about allergies, medications, or chronic conditions. Arrange for someone to drive them home if sedated. What to Expect After Endoscopy Procedure Rest for the remainder of the day. Avoid heavy meals immediately; start with light food. Do not drive or operate machinery for 24 hours if sedated. Contact a doctor if you experience severe pain, persistent bleeding, or fever. Conclusion: Endoscopy is a safe, effective, and essential tool in modern healthcare. It plays a key role in diagnosing digestive conditions, detecting cancer early, and even treating problems in one procedure. With colorectal cancer on the rise in Malaysia, colonoscopy is strongly recommended for those aged 50 and above, or younger if at high risk. The ability to detect and remove polyps early makes it one of the most powerful cancer prevention tools available today. If you experience persistent gastric pain, unexplained weight loss, or rectal bleeding, speak to an MOH-certified gastroenterologist about whether endoscopy is right for you. FAQs About Endoscopy in Malaysia 1. Is endoscopy painful?No. Sedation ensures minimal discomfort. Some patients may feel mild bloating or throat irritation, which usually resolves quickly. 2. How long does recovery take?Most patients return to normal activities within 24 hours. 3. Are there risks?Complications are very rare. The risk of serious issues such as perforation is less than 0.1%. 4. How often should
