Is Stomach Balloon Cost Worth Your Affordable Investment?
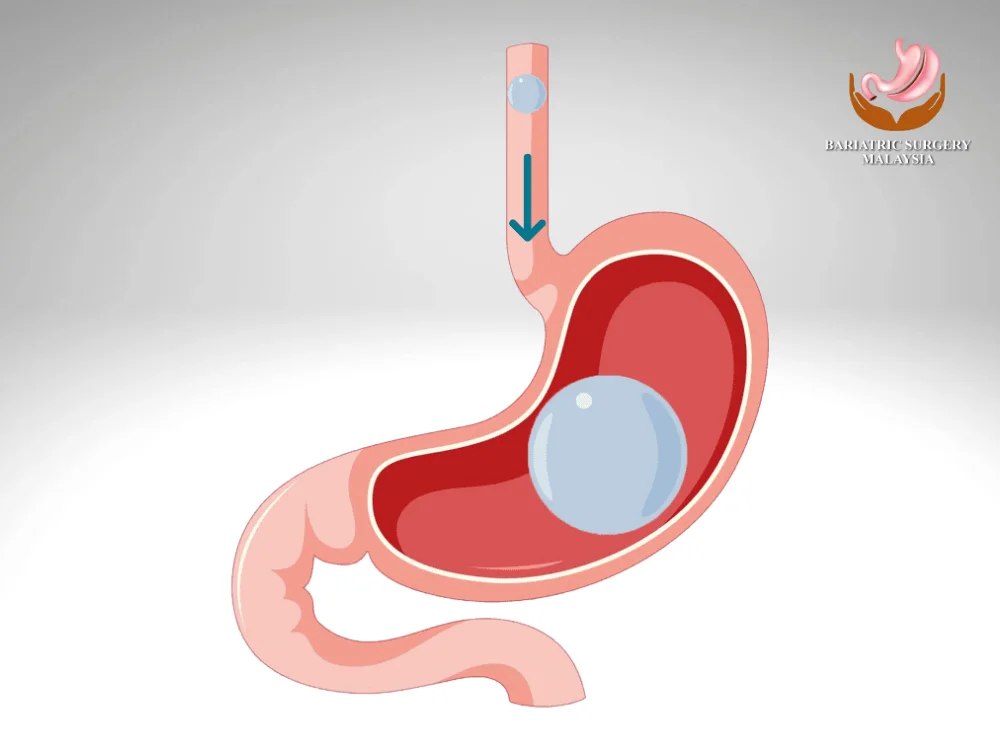
Weight loss can be a challenging journey, and for those struggling with obesity, a gastric balloon procedure offers a non-surgical alternative to traditional bariatric surgery. This temporary, minimally invasive procedure helps patients lose weight by reducing their stomach capacity, leading to faster satiety and decreased food intake. One of the primary concerns for those considering this procedure is the stomach balloon cost. The total price can vary depending on multiple factors, including the type of balloon, geographic location, and clinic reputation. In this article, we’ll break down the costs associated with this weight loss solution and determine whether it’s worth the investment. Understanding Stomach Balloon Cost What Is a Stomach Balloon? A stomach balloon, also known as an intragastric balloon, is a soft silicone balloon inserted into the stomach and inflated with saline or gas. The balloon stays in place for 4 to 12 months, restricting food intake and promoting weight loss. Unlike gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, the gastric balloon does not require surgery. The procedure is performed endoscopically and takes approximately 20 to 30 minutes. How Much Does a Stomach Balloon Cost? Average Stomach Balloon Cost Procedure The cost of a stomach (gastric) balloon varies widely depending on the country, clinic reputation, type of balloon used, and what is included in the treatment package. In general, prices are higher in Western countries and more affordable in Asia, including Malaysia. Below is a general stomach balloon cost comparison to help you understand global pricing ranges. Country Estimated Cost (Local Currency) Approximate Cost (USD) United States USD 3,000 – 7,000 USD 3,000 – 7,000 United Kingdom GBP 3,000 – 5,000 USD ~3,800 – 6,300 Canada CAD 3,500 – 6,500 USD ~2,600 – 4,800 Australia AUD 4,000 – 6,000 USD ~2,700 – 4,100 India USD 2,500 – 4,500 USD 2,500 – 4,500 Malaysia RM 12,000 – RM 25,000 USD ~2,600 – 5,400 Note: Currency conversions are approximate and may vary based on exchange rates. Stomach Balloon Cost in Malaysia (RM) In Malaysia, the stomach balloon procedure is considered more cost-effective compared to Western countries while maintaining high medical standards. On average, patients can expect to pay: RM 12,000 – RM 25,000 per balloon Prices vary based on: Type of balloon (6-month vs 12-month) Clinic reputation and specialist expertise Whether sedation and endoscopy are included Length of follow-up and weight management support Malaysia has become a popular destination for both local and international patients seeking non-surgical weight loss solutions at a more affordable price. What Is Usually Included in the Cost? A stomach balloon package may include: Initial consultation and medical assessment Balloon insertion procedure Sedation or anesthesia fees Follow-up visits and monitoring Nutritional or diet counseling Balloon removal procedure However, not all clinics include everything, so it’s important to confirm what is covered. Possible Additional or Hidden Costs Some clinics may charge separately for: Pre-procedure tests (blood tests, imaging) Medications for nausea or acid reflux Extended dietitian or lifestyle coaching programs Early removal or replacement of the balloon Asking for a full cost breakdown upfront can help avoid unexpected expenses later. Is a Cheaper Stomach Balloon Always Better? Lower cost does not always mean better value. Factors such as doctor experience, safety protocols, post-procedure support, and quality of follow-up care play a major role in both results and patient satisfaction. Choosing a reputable clinic with structured aftercare often leads to better weight loss outcomes and safer long-term results. Factors Affecting Stomach Balloon Cost Several elements influence the overall cost of a gastric balloon procedure: 1. Type of Balloon Used Different brands and models, such as Orbera, ReShape, and Spatz, have varying price points. Orbera, the most commonly used, typically costs around $6,000. 2. Geographic Location Medical procedures tend to be cheaper in countries like India and Mexico compared to the U.S. or the UK due to lower healthcare costs. 3. Clinic and Surgeon’s Expertise Highly experienced bariatric specialists may charge more due to their expertise and track record of successful procedures. 4. Additional Services Included Some clinics offer comprehensive weight loss programs that include nutritional counseling, follow-up visits, and lifestyle coaching, impacting the overall stomach balloon cost. Is the Stomach Balloon Cost Worth It? Benefits of the Gastric Balloon Procedure Non-Surgical & Reversible: Unlike other weight loss surgeries, this procedure is temporary and does not require permanent changes to the digestive system. Significant Weight Loss: Patients can lose 10–15% of their total body weight within 6 months. Improves Health Conditions: Can help reduce risks of diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea. Quick Recovery Time: Most patients resume normal activities within a few days. Potential Downsides Temporary Solution: The balloon is removed after 6 to 12 months, meaning weight regain is possible without lifestyle changes. Side Effects: Some patients experience nausea, vomiting, and stomach discomfort during the first few days. Not Covered by Insurance: Since it is considered a cosmetic weight loss procedure, many insurance providers do not cover the cost. How to Make the Stomach Balloon More Affordable Insurance & Financing Options Since most insurance plans do not cover the stomach balloon cost, patients may need to consider alternative financing options, such as: Medical Loans – Some healthcare providers offer zero-interest financing options. Health Savings Accounts (HSA) or Flexible Spending Accounts (FSA) – If eligible, you can use these funds to cover the procedure. Payment Plans – Many clinics allow patients to pay in installments instead of one lump sum. Choosing an Affordable Clinic When selecting a clinic, consider: Reputation & Reviews – Look for verified patient reviews. Transparent Pricing – Ensure there are no hidden fees. Aftercare Programs – Some clinics offer free post-procedure support, reducing long-term costs. Frequently Asked Questions FAQs 1. How long does a stomach balloon last?The balloon is typically removed after 6 to 12 months, depending on the type used. 2. Does insurance cover stomach balloon costs?Most insurance providers do not cover the procedure since it is classified as an elective weight loss method. 3. Can I get a stomach balloon for free?In some
Stroke Symptoms: The Ultimate Guide to Spotting the Warning Signs Early
Ever had that moment where you’re not sure if something is a “wait and see” situation or a “call 911 right now” situation? When it comes to stroke symptoms, there is no middle ground. A stroke is a medical emergency where every second literally translates to brain cells saved or lost. Whether it’s a sudden numbness or a weird change in your vision, knowing how to identify the signs can be the difference between a full recovery and long-term disability. 5 Key Takeaways on Stroke Symptoms Time is Brain: Act immediately; clot-busting treatments are most effective within the first 3 to 4.5 hours. B.E. F.A.S.T.: Use this acronym to check Balance, Eyes, Face, Arms, Speech, and Time. Sudden Onset: The hallmark of stroke symptoms is that they appear abruptly—often like a “bolt out of the blue.” Mini-Strokes are Real: A TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack) has the same symptoms but disappears quickly; it’s a major warning of a future stroke. Don’t Drive: If you suspect a stroke, always call an ambulance rather than driving yourself to the ER. Understanding Stroke Symptoms and Why Speed Matters Google’s AI overview often highlights that a stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is blocked or a vessel bursts. This immediate lack of oxygen causes brain tissue to begin dying within minutes. Recognizing these symptoms early allows medical teams to administer life-saving interventions like thrombolytics (clot-busters) or perform mechanical procedures to restore blood flow. The sooner you get to a specialized stroke unit, the higher your chances of walking away without permanent damage. The B.E. F.A.S.T. Method: Your Quickest Diagnostic Tool While there are many potential indicators, the medical community uses a simple acronym to help everyone remember the most common neurological deficits associated with a stroke. B – Balance: Is the person suddenly dizzy, uncoordinated, or having trouble walking? E – Eyes: Is there sudden blurred vision, double vision, or a total loss of sight in one eye? F – Face: Ask them to smile. Does one side of the face droop or feel numb? A – Arms: Ask them to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward or feel weak? S – Speech: Is their speech slurred or garbled? Can they repeat a simple sentence? T – Time: If any of these signs are present, it is Time to call 911 immediately. Causes of Stroke Understanding what triggers a stroke is just as important as knowing the symptoms. Most strokes fall into two primary categories, each with distinct causes: Ischemic Stroke: This is the most common cause, accounting for about 87% of cases. It happens when a blood clot blocks an artery leading to the brain. These clots often form in arteries damaged by atherosclerosis (plaque buildup). Hemorrhagic Stroke: This occurs when a blood vessel in the brain leaks or ruptures. Common causes include uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure), over-treatment with anticoagulants, or aneurysms (weak spots in blood vessel walls). Cryptogenic Stroke: In some cases, despite extensive testing, the cause of a stroke remains unknown. According to the American Stroke Association, underlying conditions like Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)—a type of irregular heartbeat—can also cause blood to pool and form clots that travel to the brain. Atypical Stroke Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore While the “classic” signs are most common, strokes can also present with less obvious issues. These are sometimes called silent stroke symptoms because they aren’t always recognized as an emergency right away. Sudden Severe Headache: Often described as the “worst headache of your life” with no known cause. Confusion: Sudden disorientation, trouble understanding others, or memory lapses. Numbness: A “pins and needles” sensation, specifically when it’s limited to one side of the body. Nausea and Vomiting: Especially when paired with vertigo or a severe headache. How Stroke Symptoms Differ Between Men and Women Interestingly, research suggests that women may experience more “non-traditional” symptoms. While both men and women experience face drooping and arm weakness, women are more likely to report: General body weakness or fainting. Shortness of breath or chest pain. Sudden behavioral changes or hiccups. Because these symptoms can be vague, women often wait longer to seek help. If you’re in a metropolitan area like Houston or Chicago, local health systems often provide community outreach to help identify these specific signs. Identifying a “Mini-Stroke” (TIA) A Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) is often called a mini-stroke. The symptoms are identical to a full-blown stroke but usually last only a few minutes. Don’t let the short duration fool you. A TIA is a “warning stroke” that indicates a high risk of a major event in the coming days. According to the Mayo Clinic, about 1 in 3 people who have a TIA will eventually have a full stroke. Risk Factors and Prevention: Staying Ahead of the Curve You can’t control your age or family history, but many lifestyle risk factors are within your power to change. High blood pressure is the leading cause of stroke. Other factors include: High Cholesterol: Leads to plaque buildup in the arteries. Diabetes: Damages blood vessels over time. Smoking: Doubles your risk of stroke by narrowing arteries. Obesity: Increases the strain on your entire vascular system. What to Do While Waiting for Help If you are with someone showing stroke symptoms, stay calm and take these steps: Note the Time: The medical team needs to know exactly when the first symptom started. Don’t Give Medication: Do not give the person aspirin, food, or water. If it’s a hemorrhagic stroke, aspirin could make it worse. Positioning: Keep them lying on their side with their head slightly elevated if they are conscious. Summary: Every Second Counts Identifying stroke symptoms like facial drooping, slurred speech, and sudden weakness is the first step in saving a life. Remember to B.E. F.A.S.T. and never ignore the “small” signs like sudden confusion or a “thunderclap” headache. By managing your blood pressure and staying active, you can significantly reduce your risk of ever needing to use this knowledge. People Also
Bariatric Surgery: Complete Guide 2026 In Malaysia

Bariatric surgery in Malaysia provides evidence-based, MOH-regulated treatment for severe obesity and metabolic disease. Using Asian-specific BMI criteria, fellowship-trained surgeons perform procedures such as sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass with expected 60–70% excess weight loss. Costs typically range from RM25,000–RM45,000 with structured long-term follow-up. Bariatric surgery in Malaysia is a medically approved treatment for severe obesity using procedures such as sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass. Eligible patients (BMI ≥32.5 Asian criteria) typically lose 60–70% of excess weight within 18–24 months. Surgery costs range from RM25,000 to RM45,000 depending on procedure and hospital. Key Takeaways Eligibility: BMI ≥32.5 kg/m² with obesity-related disease or BMI ≥37.5 kg/m² regardless of comorbidities Main Procedures: Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass Weight Loss: 60–70% excess weight loss within 12–24 months Metabolic Benefits: Significant improvement or remission of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea Cost: RM25,000–RM45,000 depending on complexity and facility Recovery: 2–3 days hospital stay, return to work in 2–3 weeks Long-Term Success: >90% achieve ≥50% excess weight loss with structured follow-up Understanding Bariatric Surgery: Medical and Metabolic Foundation Bariatric surgery, also referred to as metabolic surgery, consists of surgical procedures designed to treat severe obesity and its associated metabolic diseases. These procedures alter gastrointestinal anatomy to achieve sustained weight loss and hormonal regulation. Unlike cosmetic weight-loss methods, bariatric surgery is a medically indicated treatment recognised by international bodies including IFSO, ASMBS, and the Asia-Pacific Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery Society. Mechanisms of Action Bariatric surgery works through three primary mechanisms: Restriction – reduces stomach capacity, limiting food intake Hormonal Modulation – decreases hunger hormones (especially ghrelin) and improves insulin sensitivity Malabsorption (select procedures) – limits calorie and nutrient absorption These changes explain why surgery consistently outperforms diet and medication alone for long-term obesity management. Asian-Specific Obesity Classification Asian populations develop metabolic diseases at lower BMI levels due to higher visceral fat and insulin resistance. Malaysia follows adjusted thresholds: BMI ≥32.5 kg/m² with obesity-related disease BMI ≥37.5 kg/m² regardless of comorbidities This approach aligns with regional consensus guidelines and improves early intervention outcomes. Who Qualifies for Bariatric Surgery in Malaysia? Eligibility is determined through a multidisciplinary assessment involving surgeons, physicians, dietitians, and psychologists. Primary Eligibility Criteria You may qualify if you have: Type 2 diabetes Hypertension Dyslipidemia Obstructive sleep apnea MASLD (fatty liver disease) Heart or kidney disease Severe joint disease affecting mobility Patients must also demonstrate failed supervised weight-loss attempts for at least 6 months. Additional Medical Requirements Psychological evaluation to confirm readiness for lifestyle change Nutritional assessment and correction of deficiencies Smoking, alcohol, and substance cessation prior to surgery Age typically between 18–65 years (case-by-case exceptions apply) Pre-Surgical Medical Screening Before surgery, patients undergo comprehensive testing: Full blood count and metabolic panel Liver and kidney function tests ECG and cardiac evaluation Sleep study (if apnea suspected) Upper endoscopy Nutritional deficiency screening These tests establish safety, optimise outcomes, and reduce peri-operative risks. Types of Bariatric Surgery Available in Malaysia Most bariatric procedures in Malaysia are performed laparoscopically, offering faster recovery, smaller incisions, and reduced complication rates. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG) Sleeve gastrectomy removes approximately 75–80% of the stomach, forming a narrow gastric tube. Benefits: Significant appetite reduction Lower ghrelin hormone production No intestinal bypass Lower long-term vitamin deficiency risk Expected Outcomes: 60–70% excess weight loss Strong improvement in insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome This is the most commonly performed bariatric procedure in Malaysia in 2026. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) Gastric bypass creates a small gastric pouch and reroutes food to the lower small intestine. Advantages: Strong appetite suppression Highest diabetes remission rates Effective for severe reflux disease Considerations: Lifelong vitamin supplementation required Higher nutritional monitoring needs Studies published in JAMA Surgery show diabetes remission in over 60% of patients at 5 years. Advanced Procedures: BPD/DS and SADI-S Reserved for patients with very high BMI (>50) or complex metabolic disease. Procedure Excess Weight Loss Diabetes Remission Vitamin Risk Sleeve Gastrectomy 60–70% Moderate–High Low–Moderate Gastric Bypass 65–75% High Moderate–High BPD/DS / SADI-S 70–80% Very High High Revision Bariatric Surgery Revision surgery addresses inadequate weight loss, weight regain, reflux, or complications from prior procedures. Common revisions include: Band to sleeve or bypass Sleeve to gastric bypass Correction of pouch dilation These procedures require high surgical expertise and careful patient selection. Is Bariatric Surgery Safe? Modern bariatric surgery has safety profiles comparable to gallbladder surgery or joint replacement. Short-Term Risks (Overall <5%) Bleeding Infection Blood clots Anastomotic leaks Hernias Risk is significantly lower in high-volume centers with experienced teams. Long-Term Considerations Nutritional deficiencies Dumping syndrome (mainly bypass) Gallstones due to rapid weight loss Excess skin Lifelong monitoring mitigates nearly all long-term risks. Cost of Bariatric Surgery in Malaysia (2026) Average Price Ranges Sleeve Gastrectomy: RM28,000–RM38,000 Gastric Bypass: RM32,000–RM45,000 BPD/DS or SADI-S: RM40,000–RM55,000 Revision Surgery: RM35,000–RM50,000 Additional Costs Pre-operative tests: RM2,000–RM5,000 Vitamins and supplements: RM100–RM200/month Follow-up blood tests Optional body contouring surgery Insurance Coverage in Malaysia Most local policies exclude bariatric surgery unless strict medical necessity is proven. Some corporate or international plans offer partial coverage. Approval improves with: Documented obesity-related disease Long-term failed medical therapy Specialist letters Pre-authorization requests Recovery and Weight Loss Timeline Hospital Stay 2–3 days (sometimes 1 day) Return to Work Desk work: 2 weeks Physical jobs: 4–6 weeks Weight Loss Phases 0–3 months: Rapid loss (15–25 kg common) 3–12 months: Steady metabolic loss 12–24 months: Plateau and stabilization Most patients reach lowest weight by 18–24 months. Long-Term Success and Maintenance Success is defined as: ≥50% excess weight loss Sustained metabolic improvement Normal regain: 5–10% of lost weight Prevention strategies: Protein-first nutrition Regular exercise (150 min/week) Lifelong vitamin compliance Scheduled follow-ups Health Benefits Beyond Weight Loss Type 2 Diabetes: 60–80% remission or improvement Hypertension & Cholesterol: Reduced medication needs Sleep Apnea: CPAP often discontinued Joint Pain: Improved mobility Fatty Liver Disease: Reversal common Special Considerations for Malaysian Patients Asian-specific BMI thresholds Cultural dietary adaptation Ramadan fasting guidance post-recovery Halal-certified supplements Frequently Asked Questions 1. How much weight can I lose with bariatric surgery in Malaysia? Most patients lose 60–70% of excess body weight within
Eligibility for Bariatric Surgery in Malaysia: Who Qualifies?
What’s Eligibility for Bariatric Surgery for Malaysian? Bariatric surgery is a safe, effective treatment for severe obesity in Malaysia, helping patients lose weight and improve health conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure. Eligibility depends on BMI, obesity-related complications, age, and commitment to lifestyle changes. A certified surgeon and thorough evaluation are essential before surgery. What is Bariatric Surgery? Bariatric surgery, also called weight-loss surgery, reduces stomach size or changes digestion to promote weight loss. Common procedures include gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding. It’s not cosmetic; it’s a clinically proven treatment for obesity and related health problems like diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea. Who Qualifies for Bariatric Surgery in Malaysia? Eligibility is guided by medical guidelines from the Malaysian Ministry of Health and international bariatric societies. Candidates generally meet the following criteria: 1. Body Mass Index (BMI) Requirements BMI ≥ 40 kg/m² – severe obesity, even without complications. BMI 35–39.9 kg/m² – with at least one obesity-related condition (diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea). BMI 30–34.9 kg/m² – considered if serious metabolic disease exists and conventional weight-loss methods have failed. 2. Obesity-Related Health Conditions Candidates with conditions worsened by obesity may qualify, including: Type 2 diabetes Hypertension (high blood pressure) Dyslipidemia (high cholesterol) Sleep apnea or breathing difficulties Osteoarthritis affecting mobility 3. Age Criteria Typically, candidates are 18–65 years old. Younger or older patients may be considered if medically necessary and closely supervised. 4. Previous Weight-Loss Attempts Surgery is recommended only after non-surgical methods like diet, exercise, and medications have failed. Demonstrates commitment to lifestyle change, which is essential for long-term success. 5. Psychological Evaluation Candidates undergo psychological assessment to ensure realistic expectations. Helps identify mental health issues that may affect surgery outcomes, like depression or eating disorders. 6. Medical Clearance Pre-operative tests evaluate heart, lung, liver, and kidney function. Helps surgeons identify potential risks and ensure patient safety. Preparing for Bariatric Surgery Diet and Exercise: A structured pre-surgery program is often required. Lifestyle Counseling: Education on nutrition, portion control, and long-term habits. Support System: Family or peer support improves recovery and adherence. At Bariatric Surgery Malaysia Centre, certified surgeons follow international guidelines, providing thorough assessments, pre-surgery counseling, and post-operative support to ensure safe, effective bariatric surgery outcomes for patients across Malaysia. Risks and Considerations Bariatric surgery is generally safe but not risk-free: Nutritional deficiencies (iron, vitamin B12, calcium) Surgical complications (bleeding, infection, leakage) Weight regain if lifestyle changes are not maintained A certified bariatric surgeon will discuss benefits versus risks and tailor the procedure to your needs. FAQ: Eligibility for Bariatric Surgery in Malaysia 1. Can anyone with obesity get bariatric surgery?No. Candidates must meet BMI thresholds, have obesity-related health conditions, and commit to lifestyle changes. 2. What age is required for bariatric surgery?Typically 18–65 years, though exceptions exist under close medical supervision. 3. Do I need to try diet and exercise first?Yes. Surgery is considered after conventional weight-loss methods fail. 4. Are there health conditions that make me ineligible?Severe heart, liver, or kidney disease may pose risks. Psychological conditions may require treatment before surgery. 5. How is eligibility assessed?Through BMI measurement, health screening, blood tests, psychological evaluation, and lifestyle assessment by a certified bariatric surgeon. 6. Can I lose weight without surgery if I don’t qualify?Yes. Diet, exercise, behavioral therapy, and medications may help manage weight and improve health outcomes. 7. Is bariatric surgery safe in Malaysia?Yes. When performed by certified surgeons in accredited hospitals, bariatric surgery is safe and effective, with proper pre- and post-operative care. Dr. Navin Mann, Bariatric Surgeon “As a bariatric surgeon, I believe eligibility for bariatric surgery should be based on a thorough medical assessment, not just weight. Ideal candidates are those with a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health issues, who have struggled with traditional weight-loss methods, and are committed to lifelong lifestyle changes. Surgery is a powerful tool to improve health and quality of life, but success depends on careful evaluation, patient motivation, and ongoing support.”
Types of Bariatric Surgery Explained: Which One Is Right for You?
Bariatric surgery includes several procedures that help patients lose weight safely and improve health. Each type—gastric sleeve, gastric bypass, adjustable gastric band, and BPD/DS—offers unique benefits, from appetite reduction to metabolic improvement. Choosing the right surgery depends on your health, goals, and lifestyle, guided by a certified surgeon. Understanding Bariatric Surgery Bariatric surgery, or weight-loss surgery, helps people with obesity lose weight when lifestyle changes aren’t enough.It works by restricting the stomach, reducing calorie absorption, or changing hormones that control appetite.Surgery is usually recommended for adults with a BMI ≥35, or ≥30 with obesity-related conditions.These procedures can improve health, mobility, and overall quality of life. At Bariatric Surgery Malaysia Centre, our certified bariatric surgeons, Dr. Navin Mann provide personalized treatment plans for obesity. Using evidence-based bariatric surgery techniques, we ensure safe weight loss, improved metabolism, and long-term health benefits for patients across Malaysia. Types of Bariatric Surgery Gastric Sleeve (Sleeve Gastrectomy) Gastric sleeve removes about 75–80% of the stomach, leaving a smaller tube-shaped stomach.This reduces the amount of food you can eat and lowers ghrelin, the hunger hormone.Patients usually experience steady, significant weight loss and improved energy levels.It preserves normal digestion and has a lower complication rate than more complex surgeries. Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y) Gastric bypass creates a small stomach pouch and reroutes part of the small intestine.This reduces food intake, limits calorie absorption, and changes gut hormones to control appetite.Patients often lose weight rapidly and see improvements in diabetes, blood pressure, and cholesterol (study).It is especially effective for people with severe obesity or metabolic conditions. Adjustable Gastric Band (Lap-Band) The adjustable gastric band uses a silicone band around the upper stomach to limit food intake.It slows passage of food, reduces portion sizes, and is reversible without changing digestion.Weight loss is slower and gradual, which suits patients who prefer a steady lifestyle approach.The risk of nutrient deficiencies is low, and ongoing adjustments help control eating habits. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS) BPD/DS combines sleeve gastrectomy with significant intestinal bypass for maximum weight loss.It profoundly alters hormones, appetite, and metabolism, improving insulin sensitivity and diabetes.Patients achieve the greatest total weight loss and long-term metabolic benefits.Lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation is essential to prevent deficiencies. Choosing the Right Procedure Choosing the best surgery depends on your health, weight-loss goals, and lifestyle.Consider your BMI, existing medical conditions, and how quickly you want to lose weight.Surgical risk tolerance and ability to follow post-operative diet and supplementation are key.A certified bariatric surgeon and multidisciplinary team will guide you to the most suitable option. Benefits of Bariatric Surgery Types Gastric Sleeve: steady weight loss, reduced hunger, preserved digestion, lower complication risk.Gastric Bypass: rapid weight loss, diabetes improvement, better heart health, hormonal regulation.Adjustable Band: gradual weight loss, portion control, reversible, low risk of nutrient deficiencies.BPD/DS: maximum weight loss, strong metabolic improvement, hormonal benefits, long-term results. Dr. Navin Mann: “As a bariatric surgeon, I’ve seen how different types of bariatric surgery can transform patients’ lives. Gastric sleeve, gastric bypass, adjustable gastric band, and BPD/DS each offer unique benefits depending on health needs and weight-loss goals. My goal is to guide patients safely, helping them achieve sustainable weight loss and improved overall health through evidence-based, personalized care.” FAQs About Types of Bariatric Surgery 1. Which surgery offers the fastest weight loss?BPD/DS and gastric bypass usually provide the most rapid, significant weight loss. 2. Which surgery is safest with lowest complications?Gastric sleeve and adjustable gastric band have lower complication rates and are less invasive. 3. Are all surgeries reversible?Adjustable gastric band is reversible. Sleeve, bypass, and BPD/DS are generally permanent. 4. Will I need vitamins after surgery?Yes. Bypass and BPD/DS require lifelong supplementation. Sleeve may need some vitamins, band minimal. 5. How do I know which type is right for me?A certified bariatric surgeon and multidisciplinary team will evaluate your health, goals, and lifestyle to guide the choice.
How Bariatric Surgery Works: Mechanisms and Benefits
The Questions Is, How Bariatric Surgery Works? Bariatric surgery is a proven obesity treatment that helps patients lose weight safely by reducing stomach size or altering digestion. It improves metabolism, regulates appetite hormones, and lowers the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and other obesity-related conditions. Performed by certified surgeons, it combines medical care, lifestyle guidance, and long-term monitoring. What Is Bariatric Surgery? Bariatric surgery, also called weight-loss surgery, is a medical procedure designed to help people with obesity lose weight when lifestyle changes alone are insufficient. It works by reducing stomach volume or rerouting the digestive system, limiting food intake and nutrient absorption. Common types include: Gastric Sleeve (Sleeve Gastrectomy): Removes part of the stomach to reduce capacity. Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y): Bypasses part of the stomach and small intestine to decrease calorie absorption. Adjustable Gastric Band: A silicone band tightens the upper stomach to slow food passage. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS): Combines sleeve and bypass for maximum weight loss in severe obesity. How Bariatric Surgery Work and Helps With Weight Loss Bariatric surgery works by supports weight loss through several mechanisms: Restrictive Effect: Smaller stomach limits how much food you can eat. Malabsorptive Effect: Some surgeries reduce nutrient absorption, decreasing calorie intake. Hormonal Changes: Surgery alters gut hormones like ghrelin, leptin, and GLP-1, reducing appetite and improving metabolism. Metabolic Improvement: Many patients experience better blood sugar control, reduced insulin resistance, and lower cholesterol levels. Diabetes Improvement: Many patients achieve remission of type 2 diabetes within months. A 2021 systematic review reported up to 70% of patients experienced diabetes remission after bariatric surgery (NCBI) Health Benefits of Bariatric Surgery Beyond weight loss, bariatric surgery offers multiple medical benefits: Diabetes Improvement: Many patients achieve remission of type 2 diabetes within months. Cardiovascular Health: Blood pressure and cholesterol levels often improve. Joint Relief: Reduced body weight decreases stress on knees, hips, and spine. Sleep Apnea Reduction: Less fat around the airway improves breathing during sleep. Long-Term Weight Maintenance: Surgery combined with lifestyle changes produces sustained results. Bariatric Surgery in Malaysia Malaysia offers world-class bariatric programs with certified surgeons and multidisciplinary teams. Pre-surgery assessments include: Comprehensive medical evaluation and lab tests. Nutritional and psychological counseling. Personalized surgical planning. Post-operative care is essential and includes diet modification, exercise, vitamin supplementation, and regular follow-up to monitor weight, nutrition, and metabolic health. Dr. Navin Mann’s Perspective:“As a bariatric surgeon, I’ve seen firsthand how transformative weight-loss surgery can be—not just for shedding pounds, but for improving overall health and quality of life. Every patient’s journey is unique, and surgery is just one part of a lifelong approach. With careful planning, ongoing support, and lifestyle changes, bariatric surgery can dramatically reduce the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and joint problems. My goal is always to empower patients with safe, evidence-based treatments that help them regain control over their health.” Risks and Considerations While generally safe, bariatric surgery carries potential risks: Infection, bleeding, or adverse reaction to anesthesia. Nutrient deficiencies if supplementation is neglected. Dumping syndrome (rapid gastric emptying) in some procedures. Need for revision surgery in rare cases. Choosing a certified bariatric surgeon and following post-operative guidance minimizes complications and ensures optimal outcomes. FAQs About How Bariatric Surgery Works 1. Who is eligible for bariatric surgery?Adults with a BMI ≥35, or ≥30 with obesity-related conditions like diabetes or hypertension, may be considered. A full medical and psychological assessment is required. 2. How soon will I lose weight after surgery?Most patients lose 20–35% of total body weight in the first 6–12 months. Long-term results depend on diet, exercise, and lifestyle adherence. 3. Is bariatric surgery safe?Yes, when performed by experienced surgeons in accredited hospitals. Complication rates are low, and serious risks are rare. 4. Will I need vitamins after surgery?Yes, lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation is essential, especially after malabsorptive procedures like gastric bypass or BPD/DS. 5. Can bariatric surgery improve diabetes?Yes, many patients experience significant improvement or remission of type 2 diabetes due to hormonal and metabolic changes.
Hipoglisemia: Punca, Tanda Awal, Rawatan & Pencegahan Lengkap

Hipoglisemia ialah keadaan gula darah rendah yang boleh berlaku pada pesakit diabetes dan individu tanpa diabetes. Ia berpunca daripada ketidakseimbangan insulin dan hormon glukagon. Rawatan segera penting bagi mencegah komplikasi serius seperti pengsan, sawan, atau koma. Bariatric Surgery Malaysia menawarkan pembedahan bariatrik selamat dan terbukti, dikendalikan pakar berpengalaman seperti Dr. Navin Mann, membantu mengawal berat badan dan mengurangkan risiko hipoglisemia secara berkesan. Apakah Itu Hipoglisemia? Hipoglisemia berlaku apabila paras glukosa dalam darah turun di bawah paras normal, biasanya kurang daripada 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Glukosa ialah sumber tenaga utama otak. Apabila parasnya terlalu rendah, fungsi otak dan sistem saraf akan terjejas dengan cepat. Walaupun hipoglisemia sering dikaitkan dengan diabetes, ia juga boleh berlaku pada individu tanpa diabetes, terutamanya dalam keadaan puasa lama, gangguan hormon, atau penyakit tertentu. Bagaimana Badan Mengawal Gula Darah? Paras gula darah dikawal oleh beberapa hormon utama: Insulin – menurunkan gula darah dengan membantu glukosa masuk ke dalam sel Glukagon – menaikkan gula darah dengan merangsang pelepasan glukosa dari hati Adrenalin & kortisol – membantu menaikkan gula darah semasa stres atau kecemasan Hipoglisemia berlaku apabila insulin terlalu tinggi atau glukagon gagal bertindak balas dengan mencukupi, menyebabkan paras glukosa jatuh ke tahap berbahaya. Jenis-Jenis Hipoglisemia 1. Hipoglisemia Berkaitan Diabetes Jenis paling biasa, terutamanya dalam kalangan: Pesakit diabetes jenis 1 Pesakit diabetes jenis 2 yang menggunakan insulin atau ubat tertentu Ia boleh berlaku akibat dos ubat berlebihan, terlepas makan, atau aktiviti fizikal yang tidak dirancang. 2. Hipoglisemia Reaktif (Selepas Makan) Berlaku 2–4 jam selepas makan Disebabkan tindak balas insulin berlebihan Lebih kerap berlaku pada individu dengan gangguan toleransi glukosa 3. Hipoglisemia Puasa Berlaku selepas berpuasa lama atau tidak makan Boleh berkait dengan penyakit hati, buah pinggang, atau gangguan hormon Punca Hipoglisemia Antara punca utama termasuk: Dos insulin atau ubat diabetes terlalu tinggi Terlepas atau lewat makan Senaman berat tanpa pengambilan karbohidrat mencukupi Pengambilan alkohol tanpa makanan Penyakit hati atau buah pinggang Gangguan hormon seperti: Penyakit Addison Hipopituitarisme Ketumbuhan jarang seperti insulinoma (tumor penghasil insulin) Tanda dan Gejala Hipoglisemia Gejala Awal (Tindak Balas Hormon Stres) Menggigil Berpeluh sejuk Degupan jantung laju Rasa lapar melampau Kebimbangan tiba-tiba Gejala Lanjutan (Otak Kekurangan Glukosa) Pening atau sakit kepala Kekeliruan dan sukar berfikir Percakapan tidak jelas Penglihatan kabur Perubahan tingkah laku Gejala Teruk Jika tidak dirawat segera: Pengsan Sawan Koma hipoglisemia Hipoglisemia juga boleh berlaku semasa tidur, menjadikannya lebih berbahaya kerana tanda awal mungkin tidak disedari. Bagaimana Hipoglisemia Didiagnosis? Diagnosis biasanya berdasarkan Triad Whipple: Gejala hipoglisemia Bacaan gula darah rendah Kelegaan simptom selepas gula darah dinaikkan Ujian tambahan mungkin diperlukan: Ujian gula darah puasa Ujian darah hormon Pemantauan rekod gula darah harian Ujian untuk mengenal pasti gangguan hormon atau tumor Rawatan Hipoglisemia Rawatan Segera (Peraturan 15–15) Ambil 15 gram karbohidrat cepat serap, seperti: Tablet glukosa Jus buah Minuman bergula Tunggu 15 minit Periksa semula paras gula darah Ulang jika masih rendah Selepas stabil, ambil snek atau makanan seimbang untuk mengelakkan penurunan semula. Kes Teruk Suntikan glukagon Rawatan kecemasan di hospital Pencegahan Hipoglisemia Langkah pencegahan termasuk: Makan secara berkala dan seimbang Jangan terlepas waktu makan Laraskan dos insulin sebelum bersenam Elakkan alkohol berlebihan Pantau gula darah secara konsisten Gunakan Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) jika disarankan Menyimpan rekod harian (bacaan gula, dos ubat, makanan, aktiviti) sangat membantu untuk mengenal pasti corak hipoglisemia. Siapa Yang Berisiko Tinggi? Pesakit diabetes yang menggunakan insulin Warga emas Individu dengan penyakit hati atau buah pinggang Individu dengan gangguan hormon Mereka yang kerap berpuasa atau mengambil alkohol Bila Perlu Jumpa Doktor? Segera berjumpa doktor jika: Episod hipoglisemia kerap berlaku Berlaku tanpa sebab jelas Berlaku semasa tidur Disertai pengsan atau sawan Soalan Lazim (FAQ) 1. Adakah hipoglisemia boleh berlaku tanpa diabetes?Ya. Ia boleh berlaku akibat puasa lama, gangguan hormon, atau penyakit tertentu. 2. Mengapa glukagon penting dalam hipoglisemia?Glukagon membantu menaikkan gula darah apabila paras glukosa terlalu rendah. 3. Apakah ujian puasa gula darah?Ia ialah ujian untuk menilai paras glukosa selepas berpuasa bagi mengenal pasti punca hipoglisemia. 4. Adakah hipoglisemia berbahaya semasa tidur?Ya. Ia boleh berlaku tanpa disedari dan berisiko menyebabkan sawan atau koma. 5. Apakah cara terbaik mencegah hipoglisemia berulang?Pemantauan konsisten, pelarasan ubat, diet seimbang, dan pendidikan pesakit.
Endoscopy Malaysia: Types, Procedures, Benefits, and What To Expect
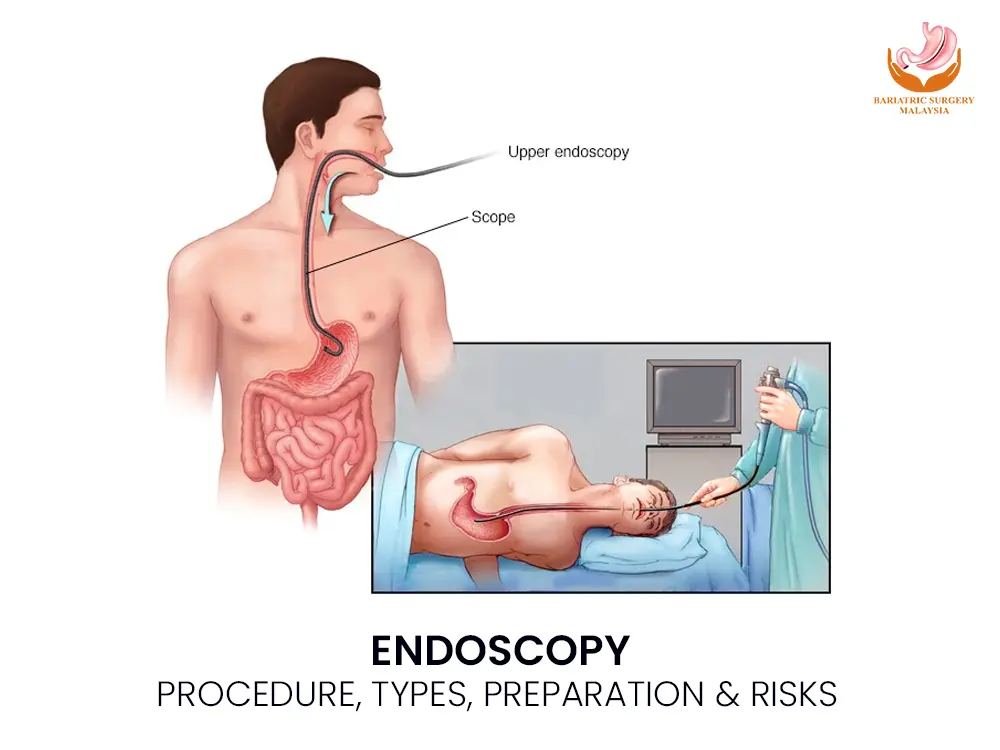
Endoscopy is a minimally invasive medical procedure that allows doctors to directly visualise the digestive tract using a flexible camera. It helps diagnose, monitor, and treat conditions such as ulcers, bleeding, inflammation, and cancer, often with same-day results, high accuracy, and a low risk of complications. What Is Endoscopy? Endoscopy is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that uses a flexible endoscope—a thin tube equipped with a high-definition camera and light source—to examine the inside of the body. It is most commonly used to assess the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract, including the oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, and rectum. Unlike imaging tests, endoscopy allows direct visualisation of the mucosal lining, enabling doctors to detect subtle abnormalities, take biopsies, and perform treatment during the same procedure. Types of Endoscopy Procedures Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (Gastroscopy) Examines the oesophagus, stomach, and duodenum.Common indications include: Chronic acid reflux (GERD) Gastritis and peptic ulcers Helicobacter pylori infection Upper gastrointestinal bleeding Barrett’s oesophagus Suspicion of upper GI cancer Colonoscopy Examines the entire colon and rectum, including the ascending, transverse, and descending colon.Used for: Colorectal cancer screening Colon polyps and precancerous lesions Chronic diarrhoea or constipation Inflammatory bowel disease Sigmoidoscopy A shorter procedure focusing on the lower part of the colon. Capsule Endoscopy Uses a swallowable camera capsule to visualise the small intestine, especially when standard endoscopy cannot reach the area. Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Combines endoscopy with ultrasound to evaluate deeper tissue layers, lymph nodes, pancreas, and nearby organs. How Endoscopy Works (Mechanism of Action) Real-time imaging via fibre-optic or digital chip technology Light transmission illuminates internal structures Carbon dioxide or air is gently insufflated to expand the organ Abnormal tissue is identified visually Biopsy forceps allow painless tissue sampling Therapeutic channels enable treatment during the procedure This direct approach makes endoscopy more accurate than scans for many digestive conditions. Why Is Endoscopy Done? Diagnostic Purposes Persistent abdominal pain Difficulty swallowing Unexplained weight loss Gastrointestinal bleeding Anaemia of unknown cause Chronic bowel habit changes Therapeutic Uses Removal of polyps (polypectomy) Control of bleeding using clips or cautery Dilatation of narrowed areas (strictures) Removal of foreign objects Targeted biopsies for cancer diagnosis Conditions Diagnosed or Treated with Endoscopy Gastritis and erosions Peptic ulcer disease Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Varices Strictures Dysplasia and precancerous lesions Inflammatory bowel disease Gastrointestinal cancers Early detection through endoscopy significantly improves treatment outcomes. Preparation Before Endoscopy Preparation depends on the procedure type: Fasting for 6–8 hours (gastroscopy) Bowel cleansing agents (polyethylene glycol solutions) for colonoscopy Review of medications, especially blood thinners Disclosure of allergies, pregnancy, or chronic medical conditions Proper preparation ensures clear visibility and accurate results. Sedation and Medications Used Most procedures use conscious sedation, allowing comfort while maintaining breathing reflexes. Common agents include: Local anaesthetic throat spray (lidocaine) Intravenous sedatives (midazolam) Analgesics (fentanyl) Vital signs are continuously monitored throughout the procedure. Is Endoscopy Painful? Endoscopy is generally not painful. Patients may feel mild pressure or bloating due to air insufflation. Throat irritation or temporary drowsiness after sedation is common but short-lived. Risks, Side Effects, and Safety Endoscopy is considered very safe when performed by a board-certified gastroenterologist in an accredited medical facility. Possible Risks (Rare) Bleeding after biopsy or polyp removal Gastrointestinal perforation (less than 1%) Infection Sedation-related breathing issues Most patients recover fully within hours. Aftercare and Recovery Avoid driving or operating machinery for 24 hours if sedated Resume light meals once swallowing is normal Expect mild bloating or sore throat temporarily Seek medical attention for severe pain, fever, vomiting, or bleeding Biopsy results are usually available within 3–7 days Who Should Consider Endoscopy? Endoscopy is recommended for: Adults over 45 with digestive symptoms Individuals with a family history of gastrointestinal cancer Patients with unexplained anaemia or bleeding Those with abnormal imaging or blood test results It is also a key tool for cancer screening and prevention. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Is endoscopy used for cancer screening? Yes. It detects early cancer and precancerous changes, especially in the stomach and colon. Will I be fully asleep during endoscopy? Most patients receive conscious sedation, not general anaesthesia. How accurate is endoscopy compared to CT scans? Endoscopy is more accurate for detecting mucosal disease and allows biopsy. How soon can I eat after endoscopy? Usually within a few hours, once numbness wears off. When will biopsy results be ready? Typically within 3 to 7 days. Can endoscopy treat conditions or only diagnose? It can both diagnose and treat many conditions in the same session. Conclusion: Prevention Saves Lives Whether it’s managing IBD (Crohn’s or Colitis) or performing a routine cancer screening, endoscopy is a life-saving tool. It moves the conversation from “guessing” what’s wrong to “seeing” exactly what’s wrong. Finding a problem early—especially GI cancers—makes treatment much more successful.
Rintangan Insulin: Punca, Gejala, Diagnosis & Rawatan Berkesan

Rintangan insulin berlaku apabila sel tubuh tidak bertindak balas dengan insulin, hormon penting untuk mengawal gula darah. Ia meningkatkan risiko diabetes jenis 2, obesiti, dan penyakit jantung. Faktor gaya hidup, genetik, dan berat badan berlebihan memainkan peranan. Dengan pemakanan seimbang, senaman, dan pemantauan, risiko boleh dikurangkan secara berkesan. Apa Itu Rintangan Insulin? Rintangan insulin berlaku bila sel badan kurang sensitif terhadap insulin. Insulin membantu sel menyerap gula dari darah untuk tenaga. Bila sel menjadi “tahan”, gula darah meningkat, menyebabkan pankreas bekerja lebih keras. Lama-kelamaan, ini boleh membawa kepada diabetes jenis 2. Kenapa ia penting: Kawalan gula darah terganggu Meningkatkan risiko sindrom metabolik Boleh sebabkan komplikasi jantung, buah pinggang, dan saraf Punca Rintangan Insulin Rintangan insulin biasanya berpunca dari kombinasi faktor: Obesiti / berat badan berlebihan – terutamanya lemak di sekitar perut Kurang aktiviti fizikal – otot kurang guna gula, sel jadi kurang sensitif Pemakanan tidak seimbang – tinggi gula, karbohidrat halus, lemak trans Genetik & sejarah keluarga – ada orang lebih cenderung Faktor hormon / penyakit lain – contoh: PCOS, sindrom metabolik Gejala Rintangan Insulin Sering kali gejala ringan dan sukar dikesan awal. Antaranya: Kerap letih / mengantuk Sukar turunkan berat badan walaupun diet / senaman Kulit gelap di leher, ketiak, atau lipatan badan (acanthosis nigricans) Keinginan gula yang tinggi Tekanan darah tinggi Jika tidak dikawal, boleh berkembang menjadi prediabetes atau diabetes jenis 2. Diagnosis & Ujian Klinikal Doktor boleh buat beberapa ujian: Glukosa darah puasa – nilai gula semasa tidak makan HbA1c – purata gula darah 2–3 bulan Ujian toleransi glukosa (OGTT) – pantau perubahan gula selepas larutan glukosa Ujian insulin / HOMA-IR – menilai tahap insulin & sensitiviti sel Nota: HOMA-IR ≥2.5 biasanya menandakan rintangan insulin. Rawatan & Cara Mengurangkan Risiko 1. Pemakanan Sihat Pilih karbohidrat kompleks (bijirin penuh, sayur-sayuran) Tingkatkan protein & serat Hadkan gula, minuman manis, lemak trans Contoh menu harian: Sarapan: oat + susu rendah lemak + buah beri Makan tengah hari: nasi perang + ayam panggang + sayur kukus Makan malam: ikan stim + sayur hijau + quinoa 2. Senaman & Aktiviti Fizikal Senaman kardiovaskular: berjalan, berlari, berbasikal Latihan kekuatan: bina otot bantu sel guna gula lebih baik Sasarkan 150 minit aktiviti sederhana seminggu 3. Kawal Berat Badan Penurunan berat badan sedikit pun boleh tingkatkan sensitiviti insulin Fokus pada perubahan jangka panjang, bukannya diet ekstrem 4. Pemantauan & Rawatan Perubatan Periksa gula darah secara berkala Pantau tekanan darah & kolesterol Ubat-ubatan seperti Metformin boleh dipertimbangkan jika diet & senaman tidak mencukupi (ikut nasihat doktor) Komplikasi Jika Tidak Dirawat Tanpa kawalan, rintangan insulin boleh sebabkan: Diabetes jenis 2 Penyakit jantung / strok Masalah buah pinggang Sindrom metabolik Masalah hormon (contoh: PCOS) FAQ – Soalan Lazim 1. Adakah rintangan insulin sama dengan diabetes?Tidak. Rintangan insulin ialah peringkat awal; jika tidak dikawal, ia boleh berkembang menjadi diabetes jenis 2. 2. Bolehkah rintangan insulin dirawat tanpa ubat?Ya, perubahan gaya hidup (diet, senaman, kawalan berat badan) boleh memperbaiki banyak kes. 3. Adakah semua orang gemuk mengalami rintangan insulin?Tidak semua, tetapi obesiti meningkatkan risiko kerana lemak perut mengganggu sensitiviti insulin. 4. Berapa cepat perubahan gaya hidup memberi kesan?Biasanya 4–12 minggu perubahan konsisten dapat memperbaiki tahap insulin, bergantung individu. 5. Apakah makanan yang membantu sensitiviti insulin?Sayur hijau, bijirin penuh, protein tanpa lemak, kekacang, buah rendah gula, dan lemak sihat (minyak zaitun, avocado). 6. Bagaimana stres & tidur mempengaruhi insulin?Kurang tidur dan stres kronik boleh meningkatkan hormon yang menurunkan sensitiviti insulin. Kesimpulan Rintangan insulin boleh dikawal dengan pengesanan awal, diet seimbang, senaman tetap, dan pemantauan berkala. Memahami punca, gejala, dan diagnosis klinikal penting untuk mencegah diabetes dan komplikasi serius. Pendekatan holistik — gaya hidup + rawatan perubatan bila perlu — meningkatkan kesihatan jangka panjang.
OMAD Diet: One Meal a Day, Benefits, Risks & Side Effects

The OMAD diet, also called One Meal a Day, 23:1 intermittent fasting, or the Warrior diet, involves eating all calories in a single meal. It may aid weight loss, improve insulin sensitivity, and trigger autophagy. However, OMAD has risks like nutrient gaps, fatigue, and hunger. Medical guidance and careful planning are essential. What Is the OMAD Diet? OMAD fasting is an extreme form of time-restricted feeding (TRF) where all daily calories are consumed within a 1-hour eating window, followed by roughly 23 hours of fasting. The approach is sometimes called the Warrior diet. Unlike other intermittent fasting methods (like 16:8 or 14:10), OMAD is highly restrictive and focuses on when you eat rather than what you eat. Beginners often try the OMAD 30-day challenge to track OMAD results, including weight loss, mental clarity, and appetite control. How OMAD Diet Affects the Body During the long fasting window, OMAD triggers several biological processes: Insulin sensitivity improves, which may benefit blood sugar control Glycogen stores deplete, prompting metabolic switching to fat for energy Autophagy and cellular repair increase, helping the body remove damaged cells Ghrelin and leptin levels adjust, affecting hunger and fullness Human Growth Hormone (HGH) may rise, aiding muscle preservation Prolonged fasting can promote ketosis, especially on OMAD keto These processes contribute to potential weight loss, fat burning, and metabolic benefits, though effects vary widely. Read More : Diet IF Potential Benefits of OMAD Diet The OMAD diet may offer several advantages, particularly when meals are well-planned: Weight loss: Eating once often creates a caloric deficit, helping break a weight loss plateau Mental clarity: Many report improved focus during fasting Simplicity: Planning a single high protein OMAD meal or a nutrient-dense 1500–2000 calorie OMAD reduces food prep stress Metabolic health: Autophagy and hormonal benefits support overall cell and metabolic function OMAD results depend on calorie quality, macronutrient balance, and adherence to the fasting schedule. Risks and Side Effects Despite potential benefits, OMAD carries notable risks: Fatigue, dizziness, headaches, and irritability Difficulty meeting daily nutrient density and protein requirements Blood sugar fluctuations, especially for women and people with diabetes Possible slow-down in basal metabolic rate (BMR) if calories are too low The refeeding window is critical to prevent nutrient gaps. Using OMAD meal ideas that include vegetables, protein, and healthy fats is essential. Hydration and electrolytes for fasting are also important, especially during longer fasts. Mortality Risk: A 2023 study published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics indicated that consuming only one meal per day is associated with a higher risk of all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in adults aged 40 and older. Meal Planning for OMAD Diet Successful OMAD requires careful planning: 1500 calorie OMAD: Moderate weight loss 2000 calorie OMAD: Suitable for active adults High protein OMAD: Preserves muscle mass OMAD keto: Low-carb, high-fat fat-burning option Focus on macronutrient balance, vitamins, minerals, and nutrient-dense foods. Use bone broth OMAD or black coffee fasting to manage hunger during fasting hours. Best time for OMAD meal: Many people choose lunch or dinner based on work and social schedules. Consistency helps with hunger management and adherence. OMAD Diet vs Other Intermittent Fasting Methods Fasting Method Eating Window Safety 14:10 10 hours Low-risk, beginner-friendly 16:8 8 hours Moderate, sustainable OMAD / 23:1 1 hour High risk, extreme but may enhance autophagy Less extreme fasting often yields similar benefits with lower side effects. Practical Tips for Beginners Start gradually: try shorter fasts before committing to OMAD Plan meals: meal prep for OMAD ensures balanced calories and nutrients Hydrate with water, black coffee, or bone broth OMAD Listen to your body: avoid intense workouts initially; ask “Can I exercise on OMAD?” Focus on OMAD benefits like mental clarity and metabolic switching, but monitor OMAD side effects FAQ How to start OMAD? Begin with shorter fasting windows and gradually increase fasting hours while maintaining macronutrient balance. OMAD vs 16:8 fasting: OMAD is more extreme, 16:8 is easier to sustain and safer long-term. Is OMAD safe for women? Women may be more sensitive to fasting. Monitor energy, hormones, and nutrient intake. How to break an OMAD fast? Eat a balanced, nutrient-dense meal. Avoid overeating. OMAD success stories: Many report fat loss, appetite control, and better focus. Results vary depending on calories, meal quality, and consistency. Bariatric Surgery vs OMAD Diet: Which Is Right? Bariatric surgery and the OMAD diet both support weight loss, but in very different ways. Bariatric surgery is a safe, medically supervised procedure that not only reduces stomach size but also improves hunger hormones and metabolism. It can lead to significant, long-term weight loss and often improves conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea. The OMAD diet, or One Meal a Day, is a form of 23:1 intermittent fasting that can help healthy adults lose weight and boost metabolism, but it may cause fatigue, nutrient gaps, and can be hard to maintain long-term. Choosing the right approach depends on your health, goals, and guidance from a medical professional. Key Takeaway The OMAD diet can improve insulin sensitivity, support autophagy, and aid weight loss when done correctly. However, it is extreme, with risks like nutrient deficiency, fatigue, and slowed metabolism. Proper OMAD meal planning, hydration, and professional guidance are essential, especially for beginners, women, and active adults.
